Key Takeaways:
- With the federal government promising over US$360 billion in clean energy incentives under the Inflation Reduction Act, energy companies are already lining up investments.
- Some have resisted clean energy mandates.
- At a regional scale, industry leaders said, it can be easier to identify shared goals.
- However, as utilities from more far-flung (and less windy) states joined MISO, they challenged these initiatives as not bringing benefits to their local grids.
- Waiting for the right kind of pressure Energy leaders also said that companies are not enthusiastic about taking on risks that low-carbon energy projects will increase costs or degrade grid reliability without some kind of financial or regulatory pressure.
- For all the talk about environmental, social and governance concerns that industry leaders need to prioritize – known as ESG – we heard during the roundtable that investors are not moving much money out of energy companies whose responses to ESG concerns are not satisfactory.
With the federal government promising over US$360 billion in clean energy incentives under the Inflation Reduction Act, energy companies are already lining up investments. It’s a huge opportunity, and analysts project that it could help slash U.S. greenhouse gas emissions by about 40% within the decade.
But in conversations with energy industry leaders in recent months, we have heard that financial incentives alone aren’t enough to meet the nation’s goal of reaching net-zero emissions by 2050.
In the view of some energy sector leaders, reaching net zero emissions will require more pressure from regulators and investors and accepting technologies that aren’t usually thought of as the best solutions to the climate crisis.
‘Net-zero,’ with natural gas
In spring 2022, we facilitated a series of conversations at Penn State University around energy and climate with leaders at several major energy companies – including Shell USA, and electric utilities American Electric Power and Xcel Energy – as well as with leaders at the Department of Energy and other public-sector agencies.
We asked them about the technologies they see the U.S. leaning on to develop an energy system with zero net greenhouse gases by 2050.
Their answers provide some insight into how energy companies are thinking about a net-zero future that will require extraordinary changes in how the world produces and manages energy.
We heard a lot of agreement among energy leaders that getting to net-zero emissions is not a matter of finding some future magic bullet. They point out that many effective technologies are available to reduce emissions and to capture those emissions that can’t be avoided. What is not an option, in their view, is to leave existing technologies in the rearview mirror.
They expect natural gas in particular to play a large, and possibly growing, role in the U.S. energy sector for many years to come.
What’s behind this view, energy leaders say, is their deep degree of skepticism that renewable energy technologies alone can meet the nation’s future energy demands at a reasonable cost.
Costs for wind and solar power and for energy storage have declined rapidly in recent years. But dependence on these technologies has some grid operators worried that they can’t count on the wind blowing or sun shining at the right time – especially as more electric vehicles and other new users connect to the power grid.
Energy companies are rightly nervous about energy grid failures – no one wants a repeat of the outages in Texas in the winter of 2021. But some energy companies, even those with lofty climate goals, also profit handsomely from traditional energy technologies and have extensive investments in fossil fuels. Some have resisted clean energy mandates.
In the view of many of these energy companies, a net-zero energy transition is not necessarily a renewable energy transition.
Instead, they see a net-zero energy transition requiring massive deployment of other technologies, including advanced nuclear power and carbon capture and sequestration technologies that capture carbon dioxide, either before it’s released or from the air, and then store it in nature or pump it underground. So far, however, attempts to deploy some of these technologies at scale have been plagued with high costs, public opposition and serious questions about their environmental impacts.
Think globally, act regionally
Another key takeaway from our roundtable discussions with energy leaders is that how clean energy is deployed and what net-zero looks like will vary by region.
What sells in Appalachia, with its natural-resource-driven economy and manufacturing base, may not sell or even be effective in other regions. Heavy industries like steel require tremendous heat as well as chemical reactions that electricity just can’t replace. The economic displacement from abandoning coal and natural gas production in these regions raises questions about who bears the burden and who benefits from shifting sources of energy.
Opportunities also vary by region. Waste from Appalachian mines could boost domestic supplies of materials critical to a cleaner energy grid. Some coastal regions, on the other hand, could drive decarbonization efforts with offshore wind power.
At a regional scale, industry leaders said, it can be easier to identify shared goals. The Midcontinent Independent System Operator, known as MISO, which manages the power grid in the upper Midwest and parts of the South, is a good example.
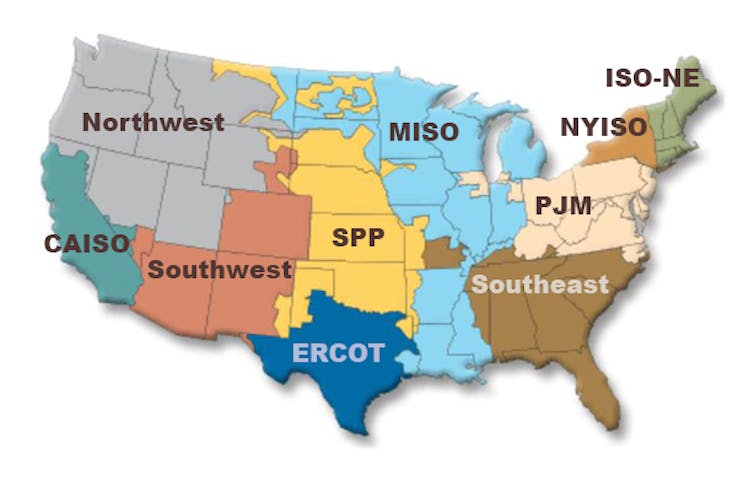
When its coverage area was predominantly in the upper Midwest, MISO could bring regional parties together with a shared vision of more opportunities for wind energy development and higher electric reliability. It was able to produce an effective multistate power grid plan to integrate renewables.
However, as utilities from more far-flung (and less windy) states joined MISO, they challenged these initiatives as not bringing benefits to their local grids. The challenges were not successful but have raised questions about how widely costs and benefits can be shared.
Waiting for the right kind of pressure
Energy leaders also said that companies are not enthusiastic about taking on risks that low-carbon energy projects will increase costs or degrade grid reliability without some kind of financial or regulatory pressure.
For example, tax credits for electric vehicles are great, but powering these vehicles could require a lot more zero-carbon electricity, not to mention a major national transmission grid upgrade to move that clean electricity around.
That could be fixed with “smart charging” – technologies that can charge vehicles during times of surplus electricity or even use electric cars to supply some of the grid’s needs on hot days. However, state utility regulators often dissuade companies from investing in power grid upgrades to meet these needs out of fear that customers will wind up footing large bills or technologies will not work as promised.
Energy companies do not yet seem to be feeling major pressure from investors to move away from fossil fuels, either.
For all the talk about environmental, social and governance concerns that industry leaders need to prioritize – known as ESG – we heard during the roundtable that investors are not moving much money out of energy companies whose responses to ESG concerns are not satisfactory. With little pressure from investors, energy companies themselves have few good reasons to take risks on clean energy or to push for changes in regulations.
Leadership needed
These conversations reinforced the need for more leadership on climate issues from lawmakers, regulators, energy companies and shareholders.
If the energy industry is stuck because of antiquated regulations, then we believe it’s up to the public and forward-looking leaders in business and government and investors to push for change.





























