Key Takeaways:
- The short answer is: No one knows who invented music.
- The earliest civilizations throughout Africa, Europe and Asia had music.
- But again, people were not singing complete melodies or songs; our modern lullabies – like “Rock-a-bye Baby” – took centuries to develop.
- In Greece, instruments like the krotola, a set of hollow blocks bound with leather, were played 2,500 years ago.
- This image shows three women in ancient Greece playing musical instruments.
- Certainly, ancient music made its listeners feel powerful emotions, just as music throughout this century and beyond will do the same.
The short answer is: No one knows who invented music.
No historical evidence exists to tell us exactly who sang the first song, or whistled the first tune, or made the first rhythmic sounds that resembled what we know today as music.
But researchers do know it happened thousands of years ago. The earliest civilizations throughout Africa, Europe and Asia had music. Back then, many believed it was a divine creation, a gift from the gods.
Indeed, gods and goddesses from many religions and mythologies are associated with music. Stories and works of art tell us that the African god Àyàn was a drummer; the Greek god Apollo played the lyre, a string instrument. In the Book of Genesis, Jubal – a descendant of Adam – is identified as the father of the harp and flute.
Scientists will probably never be able to credit one person, or even a group of people, with music’s invention. But as a musicologist – that’s someone who studies the history of music – I’ve seen many artifacts and much evidence that can help us understand how and why the ancients played music.
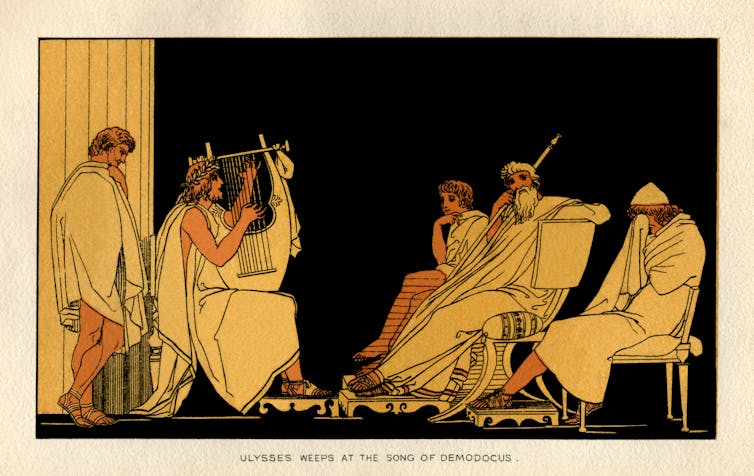

Singing
Some scholars say singing was the first kind of musical sound. Not that people back then were crooning full-length songs. Instead, they made simpler vocal sounds – perhaps just a few notes put together. If that’s true, perhaps early humans began to speak and sing at about the same time.
Why did they sing? Maybe they had an impulse to imitate something beautiful, like bird sounds. Vocal imitations of other animal sounds, however, may have been used for hunting, like a modern-day duck call.
It’s also possible singing was a way to communicate with infants and toddlers, like early versions of lullabies. But again, people were not singing complete melodies or songs; our modern lullabies – like “Rock-a-bye Baby” – took centuries to develop.
Singing in Catholic churches throughout Europe during the Middle Ages is well documented. At first there was only a single vocal melody, sung either by a soloist or a small group of male clergy. Nuns also learned to sing in convents. Later, polyphony became increasingly common – when two, three or four voices would each sing different melodies, adding to the complexity of the sound.
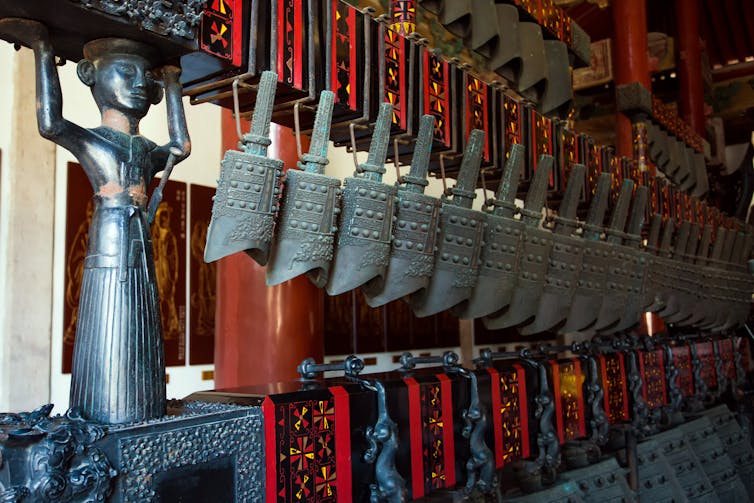

Instruments
Archaeologists have helped musicologists learn about ancient musical instruments from the artifacts they’ve uncovered. For example, they have found flutes and whistles made of bone, pottery and stone.
The archaeologists used a process known as carbon-14 dating to find out how old the bone instruments were. All living organisms – animals, plants and people – have some carbon-14 in them; when they die, the amount of carbon-14 decreases, little by little, over years, decades and centuries.
When the scientists measured how much carbon-14 was left in the flutes – which were made from the bones of large birds – they discovered some of the instruments were more than 30,000 years old!
In Japan, some ancient whistles and rattles, made of stone or clay, are about 6,000 years old. Through their small blowholes, these instruments created high, shrill tones. Those using them may have thought the sounds were somehow magical, and it’s possible they played them during religious rituals. Some of those stone whistles can still make sounds.
In China, pottery bells, which may be the ancestors to bronze bells, appeared at least 4,000 years ago. In Greece, instruments like the krotola, a set of hollow blocks bound with leather, were played 2,500 years ago. The Greeks also used finger cymbals and frame drums – similar to the kind you might use at school.
Musical instruments could also be associated with different types of people. Shepherds played the syrinx, a whistlelike instrument, known today as the pan flute. It was a simple instrument that was easy to take into the fields. The aulos was a more sophisticated woodwind instrument consisting of two pipes. Because it took more skill to play the aulos, you would need training from a teacher – or perhaps, if you were wealthy, you could just hire experienced musicians to play for you.
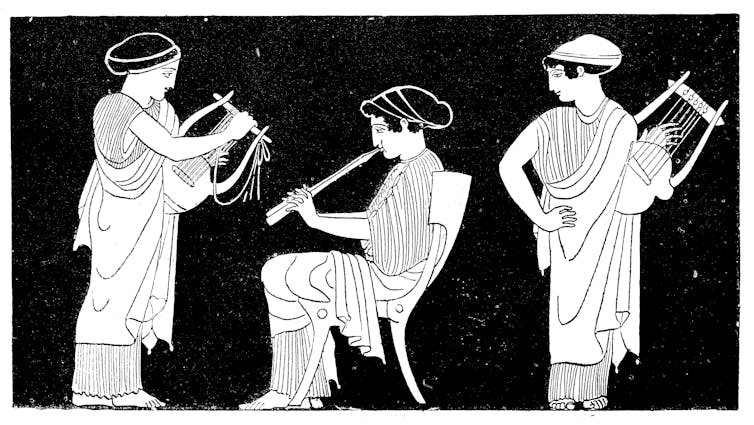

Manuscripts and artwork
In Africa, 4,000-year-old rock paintings and engravings found in Egyptian tombs show musicians playing what appear to be harps.
Greek pottery often depicts musical scenes; these images often appeared on vases and urns. The settings, though, are often unclear. Whether the musicians were part of a festival or celebration, or simply playing for their own entertainment, is not always known.
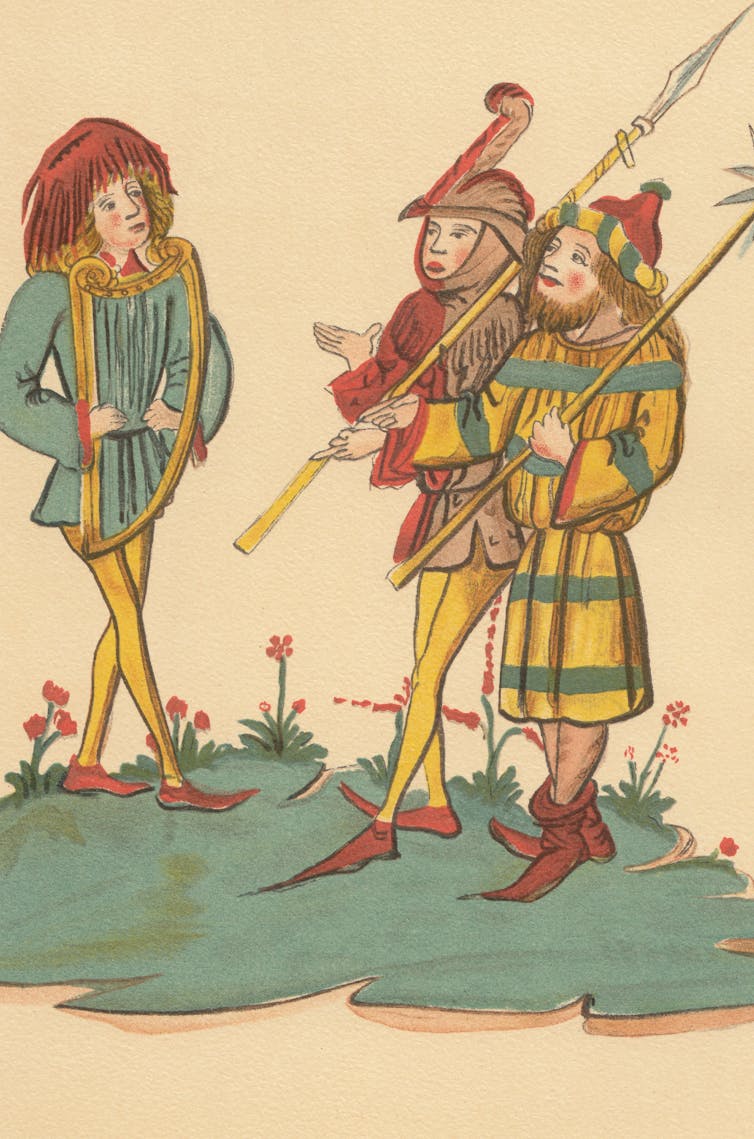
Handmade medieval manuscripts also provide clues. Illustrations with ink, and sometimes gold leaf, often show musicians playing an instrument.

A world without music
Can you imagine living today without music? I can’t. Not only does it entertain and enthrall, it allows us to communicate emotions. Music helps us celebrate joyful events and consoles us when we’re sad or in pain. Certainly, ancient music made its listeners feel powerful emotions, just as music throughout this century and beyond will do the same. Think for a moment what music in the 22nd century might sound like. And who knows? Maybe – in about 78 years – you’ll find out.