Key Takeaway
Apple unveiled its Vision Pro headset, blending VR, AR, and mixed reality. The headset uses 12 cameras and EyeSight to detect and display people in the real world, allowing users to adjust their immersion level. The Vision Pro is expected to revolutionize head-mounted devices and bring immersive technologies to mainstream use. Apple’s Vision Pro headset uses cameras, microphones, LiDAR scanner, and displays for real-world awareness, offering a wearable ecosystem for interoperable devices. Apple’s Vision Pro headset, combining iPhone, Apple Watch, and programming tools, could create new uses for augmented reality and tap into existing developers.
Apple recently unveiled its Vision Pro headset at the Worldwide Developers Conference in California. With it, Apple is venturing into a market of head-mounted devices (HMDs) – which are usually just displays, but in this case is more of a complete computer attached to your head – as well as the worlds of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR).
The new Apple product will fuel the hopes of many working on these technologies that they will some day be routinely used by the public, just as the iPhone, iPad and Apple Watch helped bring smartphones, tablets and wearable tech into mainstream use.
But what does the Vision Pro actually do, and how much mass appeal will it have?
VR immerses users in an entirely computer-generated world, isolating them to a large degree from their physical surroundings. AR superimposes computer-generated elements onto the real world while the latter remains visible, with the purpose of enhancing the context of our physical surroundings.
A term often used interchangeably with AR is mixed reality, referring to a set of immersive technologies including AR, that provide different “blends” of physical and virtual worlds. These three technologies are often collectively referred to as XR.
The blending of VR and AR seems to be a key part of Apple’s thinking, with the Vision Pro allowing users to adjust their level of immersion by deciding how much of the real world they can see. This transitioning between the two experiences will probably be a trend for future HMDs.

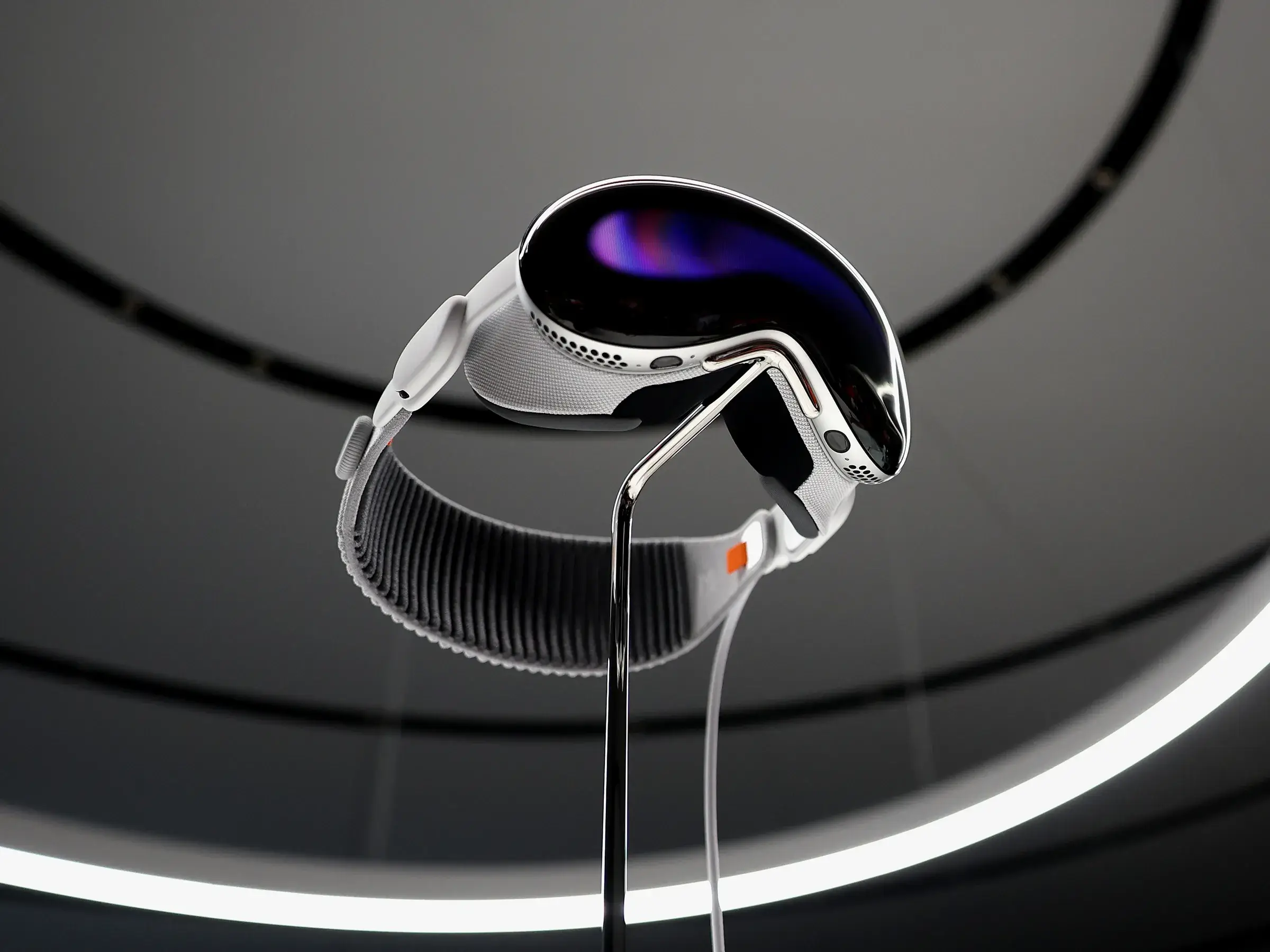
The physical world is “seen” through an array of 12 cameras located behind a ski-goggle-like glass fascia, acting as a lens. When the Vision Pro is in VR mode, people approaching you in the real world are automatically detected and displayed as they get close.
A feature called EyeSight also displays the wearer’s eyes through the glass lens when needed, to enable more natural interaction with people around them – a challenge for many HMDs.
In terms of technical specifications, the Vision Pro is impressive. It uses a combination of the M2 microchip and a new chip called the R1. M2 is running visionOS, which Apple calls its first spatial operating system, along with computer vision algorithms and computer graphics generation.
R1 processes information from the cameras, an array of microphones and a LiDAR scanner – which uses a laser to measure distances to different objects – in order to make the headset aware of its surroundings.
More importantly, the Vision Pro boasts an impressive display system with “more pixels than a 4K TV to each eye”. Its ability to track where the wearer’s eyes are looking allows users to interact with graphical elements just by looking at them. The headset can receive gesture and voice commands and features a form of 360-degree sound called spatial audio. The quoted unplugged operating time is two hours.
Wearable ‘ecosystem’
Packed, in typical Apple fashion, in curved aluminum and glass, the headset has an eye-watering price of US$3,499 (£2,819) and represents a collection of many premium features. But Apple has a history of developing products with increasingly versatile capabilities to sense what’s going on in their real-world surroundings.

Apple also focuses on making its devices interoperable – meaning they work easily with other Apple devices – forming a wearable “ecosystem”. This is what really promises to be disruptive about the Vision Pro. It is also akin to what had been promised and hoped for by pioneers in the idea of wearable computing back in the 1990s.
Combining the headset with the iPhone, which still forms the backbone of Apple’s ecosystem, and the Apple Watch could help create new uses for augmented reality. Likewise, linking the headset to many programming tools demonstrates the company’s desire to tap into an existing community of developers of augmented reality applications.
Many questions remain, however. For example, will it be able to access mixed reality applications via a web browser? What will it be like to use from an ergonomic point of view?
It’s also unclear when the Vision Pro be available outside the US or whether there will be a non-Pro version – as the “Pro” part of the title implies a more “expert”, or developer market.
The Vision Pro is a gamble, as XR is often seen as something that promises but rarely delivers. Yet, companies such as Apple and those that are probably its primary competitors in the XR domain, Meta and Microsoft, have the clout to make XR popular for the general public.
More importantly, devices such as the Vision Pro and its ecosystem, as well as its competitors could provide the foundation for developing the metaverse. This is an immersive world, facilitated by headsets, that aims for social interaction that’s more natural than with previous products.
Sceptics will say that Vision Pro and EyeSight make you appear like a scuba diver in your living room. But this could finally be the time to dive into the deep waters of XR.