There’s a workshop at the Getty Center where the paintings aren’t the stars. Instead, the frames take center stage. In this bright and airy room, empty frames hang on the walls, and tools and books line the counters. There you’d find associate conservator Gene Karakker, who retired earlier this summer, choosing from an assortment of scalpels, knives, brushes, and cleaning solutions before turning to centuries-old frames propped up on wooden stands waiting to be restored. Once they are paired with artworks and hung on the gallery walls, their job will be to protect and enhance the artworks. These frames, with their intricately carved florals, scalloped edges, and swooping curves, are triumphs of art and design in their own right.
Frames tell their own tales: about when and where the artwork was completed, the decorative styles that were popular at the time, and the artwork’s journey from artist to collector. To learn the history of a frame, then, is to learn an even richer story about the artwork itself.
We spent some time with Karraker last year to find out more about where frame design comes from and how frames make their way to the Getty. He revealed a captivating history of framing and the process Getty curators and conservators go through in order to find the perfect frame for each artwork.
“For centuries, even though a lot of frames have been discarded and they’ve been put into attics and basements, they still survived,” Karraker said, “and they still have a beauty about them.”
Why Do Artworks Have Frames?
The practice of framing artworks with wooden borders first appeared in Italian art around the 13th century. During this time, artists often painted on wooden panels. The centers of the panels were carved out so that the exterior formed a raised molding. This was called an engaged frame, and developed into moldings that were nailed directly onto the painting. These early paintings were typically religious and were built directly into the architecture of the church. The frames were usually styled after the moldings that adorned the doors and windows.
“The original purpose for the frame was simply to protect the painting,” Karraker said.
These panel paintings required multiple craftsmen. Someone would make the panel, then someone else would finish the panel, a gilder would add any gold elements, another craftsperson might add additional decoration, and then it would be handed off to the artist for painting.
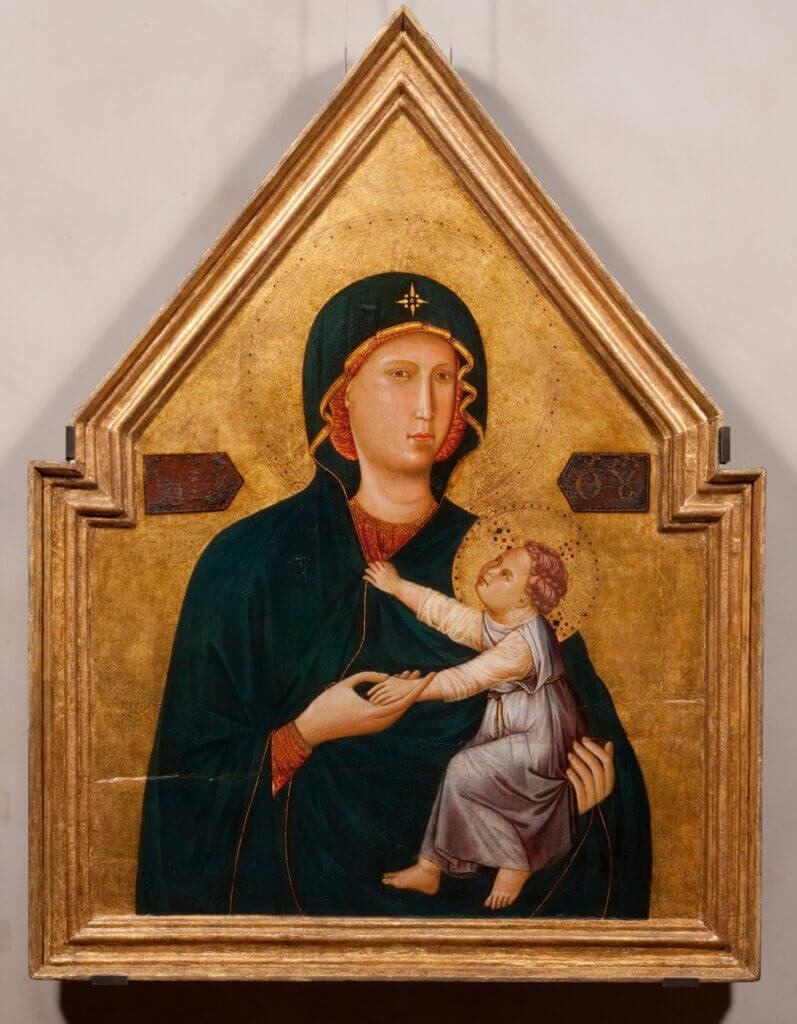

This 13th-century Italian carved and gilded frame is an example of an engaged frame. Madonna and Child, 1290–1295, Master of St. Cecilia. Tempera and gold leaf on panel, 41 1/2 × 31 1/4 in. The J. Paul Getty Museum, 2000.35
Styles and Materials
As more secular paintings emerged throughout the 16th and 17th centuries, and artists began moving away from panel paintings in favor of canvas, frames became more like what we see today.
In Europe, countries and regions had their own unique frame styles and materials that were often influenced by other styles. For example, the Italian Baroque style influenced the decorative style Louis XIII used in his palace furnishings and frames; the styles favored by subsequent kings of France such as Rococo and Neoclassical could then be glimpsed in frames made in Belgium, Italy, and beyond.

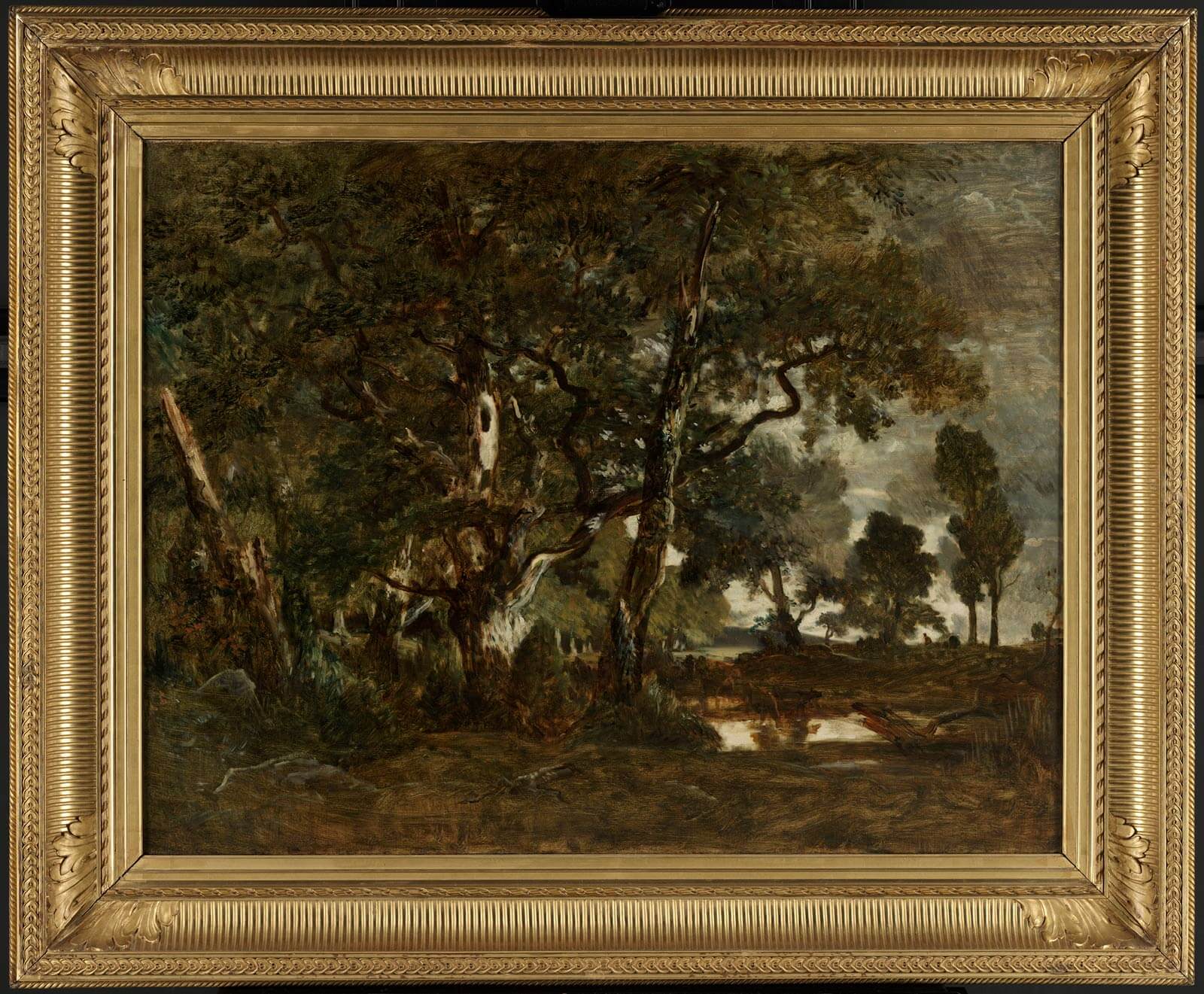
An example of a frame from the Regénce period from around 1700–1720, when design began to transition from the Baroque to Rococo style. This carved and gilded frame features a sanded flat, acanthus strapwork with scallop shell ornament, diaper recutting, and pronounced center and corner ornaments on tooled ground. A Wooded Landscape with Travelers on a Path through a Hamlet, about 1665, Meindert Hobbema and Abraham Storck. Oil on canvas, 52 1/2 × 64 3/4 in. The J. Paul Getty Museum, 2002.17
Thus, frame styles became a way for the artwork’s owner to put their own “stamp” on it. A private owner might frame a painting to match their home decor, or a museum might adopt a particular style—for example, the National Museum of Dresden, which has framed its paintings in the same style since the 18th century.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, some artists became more involved in designing frames for their own works. Impressionists rejected the artistic conventions of the day in favor of quick brushstrokes, everyday life, and the outdoors, capturing “impressions” over precise realism.
They championed the use of simpler frames they felt complemented the work better, instead of the ornate styles that were popular at the time. Simpler frames also helped differentiate their works from those of the “establishment,” a.k.a. the Paris Salon.
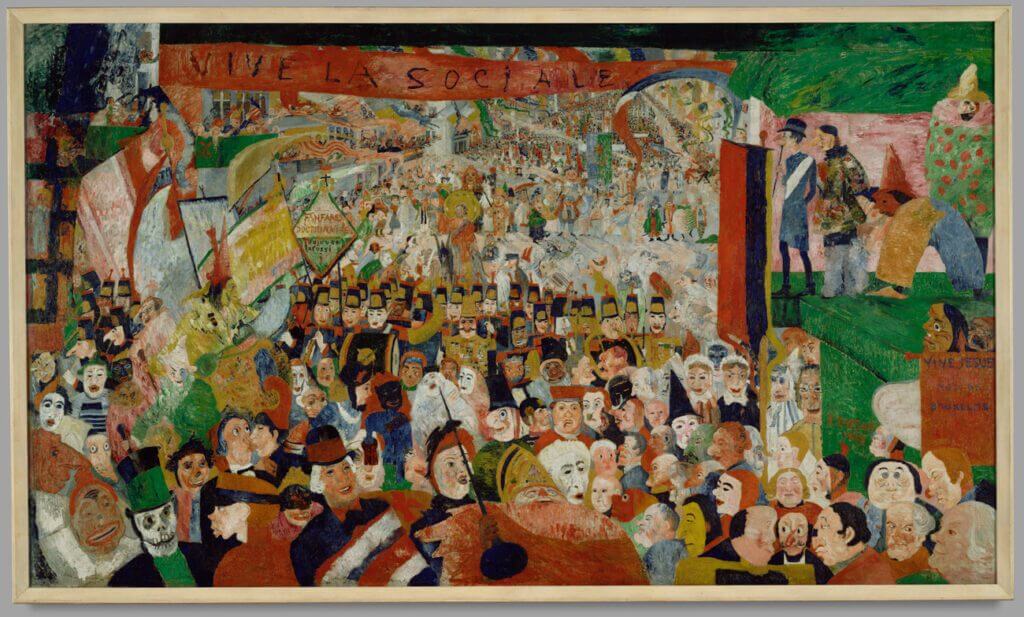

This frame, which is original to the painting, reflects the trend towards simple, unadorned frames in the late 19th century. Christ’s Entry into Brussels in 1889, 1888, James Ensor. Oil on canvas, 103 × 173 in. The J. Paul Getty Museum, 87.PA.96
However, up through the 19th century, simple, unornamented frames were not favored by collectors who continued to opt for opulent frames to make their artworks more impressive.
“When very wealthy Americans started buying Impressionist works, they wanted to make the collections look more important,” Karraker said. “So that’s the reason we’ve gotten so used to looking at Impressionist paintings in these very elaborate gilded frames because they were basically meant to make the paintings look more important. It’s probably not what the artist would have intended.”
Framing at Getty
Most pieces arrive at the Getty already framed. Sometimes, the painting is still in its original frame. But often, the painting includes a frame that was added later (sometimes centuries later) by a collector. Curators and conservators discuss where the frame came from and determine if it complements the painting and is consistent with its time and place. They might ask questions like, is the frame from the same time period as the painting itself? Is it from the same country or region as the painting? Is there any documentation that indicates the frame may be original to the painting?

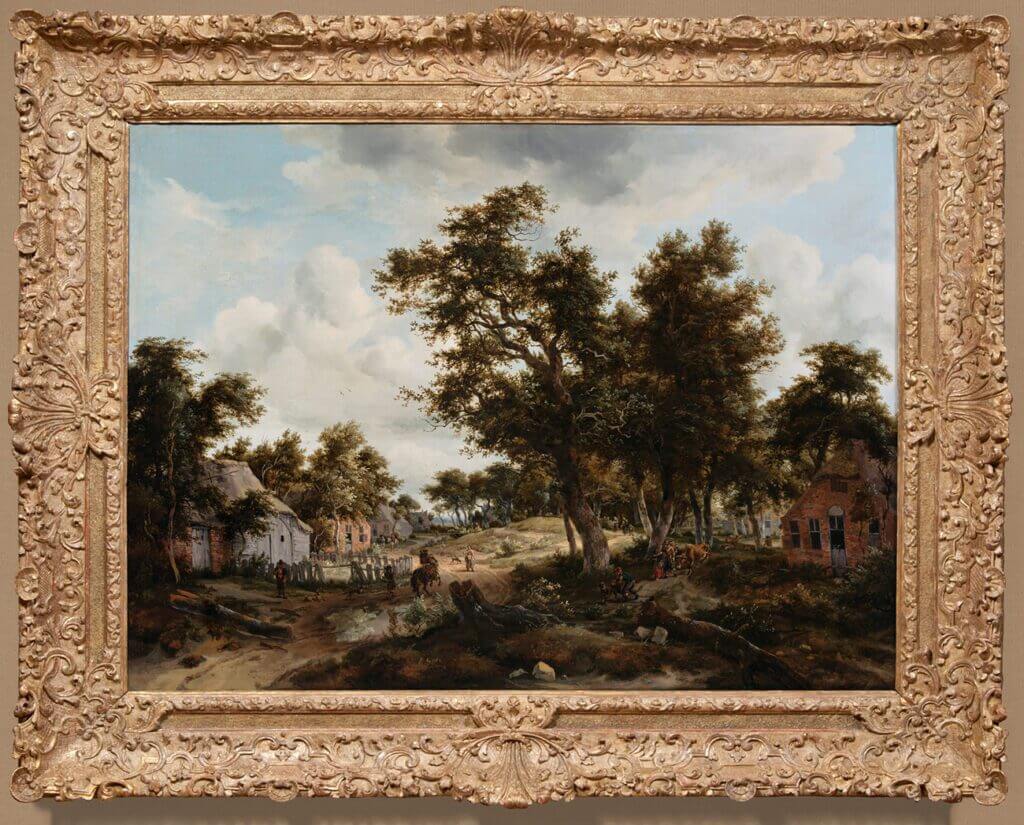
This French 18th-century carved and gilded frame features a central cartouche containing staff, crook, hat, crown, eagle, and shield, with acanthus, overlapping scales, and floret ornament running along the sight edge, carved laurel branches in small hollow, and pronounced corners with dragons and scallop shells. Charles de Saint-Albin, Archbishop of Cambrai, 1723, Hyacinthe Rigaud. Oil on canvas, 57 1/2 × 44 1/2 in. The J. Paul Getty Museum, 88.PA.136
As the frame conservator, Karraker works to restore and repair antique frames that will be displayed in the galleries, using modern power tools as well as tools that were used in the 17th century, like knives, scalpels, and files to fix missing and damaged ornamentation. Recently added to a conservator’s “toolbox” are 3D scanning and printing. If ornamentation on a frame is damaged or missing, the decorative arts conservation team can take a 3D scan of the frame and print new ornamentations out of plastic that can be painted and affixed to the frame to match preexisting ornamentations.
But sometimes, Karraker noted, it comes down to how the painting looks in the gallery. Take the Irises. Getty purchased van Gogh’s Irises from a collector in New York. The painting had been hanging in her dining room, which was covered in heavy walnut paneling, and the frame matched this décor.
“This was done just so that the painting would disappear in the setting. But when you took it out of that room and put it in the gallery, it really made absolutely no sense,” Karraker said.
The frame currently around Irises actually hails from 17th-century Italy, which doesn’t match the above criteria but the curators felt it complemented the work.

This 17th-century Italian frame was chosen by Getty curators. Irises, 1889, Vincent van Gogh. Oil on canvas, 29 1/4 x 37 1/8 in. The J. Paul Getty Museum, 90.PA.20
Ultimately, viewers should notice the art, not the frame. Karraker carefully blends repairs into the frame so it still looks aged, perhaps even a little dirty. The result: a frame that looks like it belongs with the painting and doesn’t distract from it.
“If the frame is doing its job correctly, it’ll disappear,” Karraker said.