Key Takeaway:
Sleep loss is often seen as a personal responsibility, with consumer products and media reporting treating it as a personal issue. However, recognizing sleep as a cultural issue can help us rethink our relationship with sleep and recognize how it exposes competing agendas. Literature and art can help challenge dominant visions of sleep, allowing us to see sleep as a place where values are formed and cultural debates are shaped. Sleep inequities are evident in the poor sleep of medical workers, climate disasters, and uneven rates of sleeping pill use. Literature and art can help develop a critical literacy of sleep by questioning the dominant cultural visions of sleep. By understanding the links between sleep loss and societal issues, we can be more compassionate and appreciate the importance of restful sleep. Recognizing sleep as a matter of culture allows us to think critically about the forms of power tied up with it.
Consumer products like sleep trackers and scented pillow sprays imply that sleep loss is a matter of personal responsibility, something for individuals to solve with quick tips and gadgets.
Media reports and self-help articles also tend to treat imperfect sleep as an individual problem, a failure that people need to fix by changing their habits and lifestyle. But if we think about sleep as a cultural issue, we can rethink our relationship with slumber and recognize how sleep exposes competing agendas.
Works of literature and art, for example, can teach us to challenge dominant visions of sleep, allowing us to see sleep as a place where values are formed and cultural debates are shaped.
Sleep inequities
There are many ways that sleep functions culturally as a form of inequity and power. The inequitable nature of troubles with sleep is visible through the poor sleep of medical workers, the sleep loss tied to climate disasters and uneven rates of sleeping pill use.
While some people enjoy their luxury bedding at night, others are being evicted from their homes, unsure where or how they’ll get a night’s rest.
Seeing sleep purely as a personal responsibility ignores how it is tied to social values and forms of oppression. No amount of weighted blankets, blue-light blocking glasses or aromatherapy candles can solve inherently systemic problems.

Dear Scarlet
Literature and art have always played a key role in cultural debates. Creative works can teach us to see sleep in unexpected ways, revealing the meanings of sleep in diverse contexts. They can also help us develop a critical literacy of sleep by teaching us to question the dominant cultural visions of slumber that circulate around us.
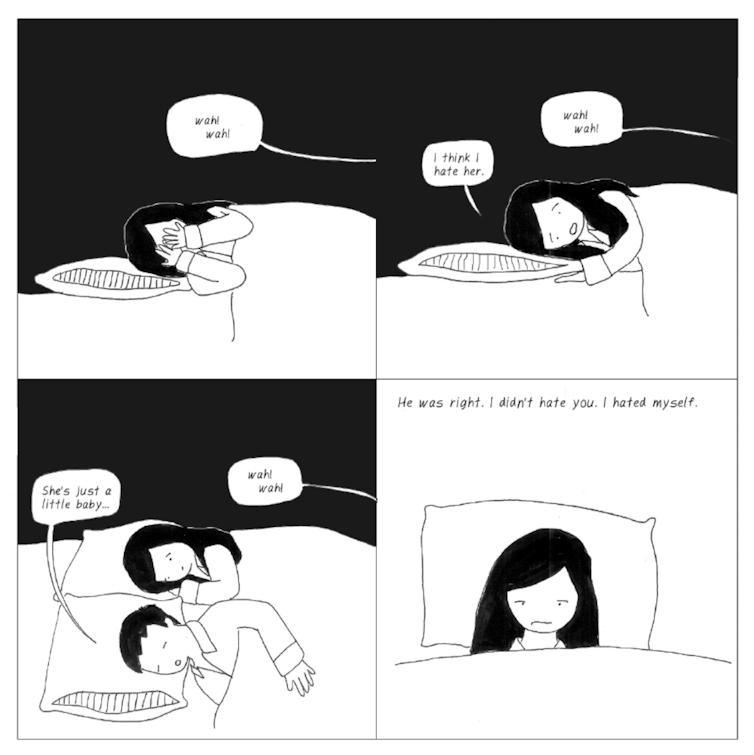
Writer and cartoonist Teresa Wong’s illustrated memoir Dear Scarlet: The Story of My Postpartum Depression shows how sleep loss for new parents can be tied to problematic cultural norms. As Wong battles overwhelming hopelessness after the birth of her first child, doctors and friends dismiss her concerns, telling her that she will get over the baby blues. Sleep deprivation makes the situation worse. Wong lies awake, filled with anxious self-doubt, and eventually thinks that her baby would be better off without her.
In one nighttime scene, the baby’s crying leads Wong to think that she hates her baby. But she decides, “I didn’t hate you. I hated myself.” This spiral of dark thoughts shows how sleep deprivation can be linked to misery for new parents, especially in the absence of support.
The starkness of Wong’s drawings reflects her blunted senses, as her inner world is drained of detail and colour. In the final panel of the sequence, Wong’s body is composed of just thirteen or so lines of ink, a bare representation that reflects her desolation. The minimal artwork conveys a big message, showing how sleep loss is tied to cultural problems around gender, health care and social isolation.

Fiction and poetry
Works of fiction and poetry can also reflect the links between sleep loss and societal issues. David Chariandy’s novel Brother follows the lives of Michael and Francis, the children of Trinidadian immigrants in Toronto. The brothers are trapped in a world of poverty and violence, and they often relive trauma in the moments when they are falling asleep.

Michael notes that Francis would “be on the edge of sleep when some terror would visit him. He’d wake screaming a deep body scream.” Of himself, Michael says, “on the edge of sleep, the shootings return to me with an attack of panic and wild vertigo.” The repeated image of the “edge” of sleep brings to mind a precipice or, perhaps, the blade of a knife that penetrates the mind.
Sleep is usually associated with peaceful rest, but by linking sleep with trauma, Brother changes what sleep means. The brothers’ nighttime panic reflects how sleep loss can be tied to social inequality and poverty, issues that go far beyond matters of personal sleep habits.
Writer Dionne Brand’s poetry considers the difficulty of sleeping when disasters are affecting others. In her book Thirsty, she writes:
“if it is late at night and quiet…
you can hear someone’s life falling apart
Most people can sleep through a siren. I can’t…
Even at a great distance
you sense its mortal discoveries.”
Sleeping through an ambulance siren can be a necessary skill in the city, but for Brand, such a sleep shows callousness toward the suffering of others. And in her poem Inventory, these anxieties extend far beyond the street outside one’s bedroom window. The speaker in this poem lies awake because people in distant places are being killed by bombs and guns: “a sleep, no, / sleep would be forgiving.”
In these poems, the cruelty of sleep is that it requires us to become skilled at indifference. Sleep is not just an everyday act. It is also a form of meaning, a contradictory symbol of anxiety and rest.
If we want to be compassionate people during our waking hours, we need to enjoy restful slumber at night. Whether or not we sleep more soundly than the people in these books, works of literature can help us understand why sleeping well is about more than buying the right mattress or debating the merits of Daylight Saving Time.
The humanities can teach us how to see sleep as a place where values take shape. And literature and art can help us decide what sleep means, or ought to mean, within the systems of power and care that shape our lives.
We need to recognize sleep as a matter of culture so that we can think critically about the forms of power tied up with it. Every sleep tells a story, and by learning to read these stories carefully, we can help each other rest a little easier.